




Tips for a Systematic Literature Review
A systematic literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a particular research topic. It is an essential component of a dissertation for a master’s degree, and it requires a significant amount of time and effort. In this blog post, we will provide some helpful tips and guidance for master’s students in the UK who are undertaking a systematic literature review dissertation.
Understand the purpose of a systematic literature review
The first step in writing a systematic literature review dissertation is to understand its purpose. The purpose of a literature review is to identify, analyze, and evaluate the existing literature on a specific research question or topic. It involves a systematic and comprehensive search of relevant literature, followed by a critical evaluation of the quality, relevance, and significance of the studies.
Develop a clear research question
A remedy here is to pick an area of interest, get into databases, research around the topic and obtain primary studies before formulating a research question. This way we would surely know the expanse of literature available and we would be able to decide upon a definite direction in which we would take the review.
The second step is to develop a clear research question that will guide your literature search and analysis. The research question should be specific, well-defined, and focused on a particular topic. It should also be broad enough to allow for a comprehensive review of the literature.
Conduct a comprehensive literature search
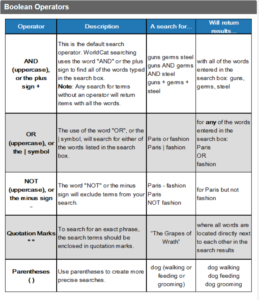
The AND operator is used to combine multiple keywords together in a way that all the keywords must be present in the search results. For example:
“apple AND banana” – this will return search results that contain both “apple” and “banana”.
The OR operator is used to combine multiple keywords together in a way that any of the keywords can be present in the search results. For example:
“apple OR banana” – this will return search results that contain either “apple” or “banana” or both.
Here are some examples of keyword strings using both AND and OR operators:
“pizza AND (pepperoni OR sausage OR mushroom)” – this will return search results that contain the word “pizza” and at least one of the words “pepperoni”, “sausage”, or “mushroom”.
“(cat OR dog OR bird) AND (food OR nutrition)” – this will return search results that contain at least one of the words “cat”, “dog”, or “bird”, as well as at least one of the words “food” or “nutrition”.
“football AND (team OR player OR coach)” – this will return search results that contain the word “football” and at least one of the words “team”, “player”, or “coach”.
The third step is to conduct a comprehensive literature search. This involves searching multiple databases, such as Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus, to identify relevant studies. You should also consider using reference lists of relevant articles and hand-searching key journals in your field.
Research strings, also known as search terms or search queries, are combinations of keywords and phrases that are used to search for relevant literature in academic databases. When individually used in databases, each search string will typically retrieve a number of papers that are relevant to the specific terms included in the search.
For example, if a researcher is interested in exploring the relationship between social media use and mental health, some search strings that they could use include:
Each of these search strings would provide a different set of papers that are relevant to the specific terms used. The researcher can then evaluate the relevance and quality of each paper to determine which ones are most useful for their research question.
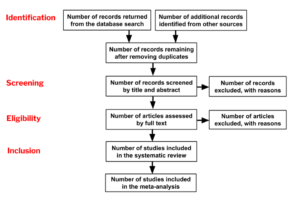
Evaluating the Quality of Literature
Once you have identified relevant literature, you need to evaluate the quality of the studies. This involves assessing the study design, sample size, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. You should also assess the credibility and validity of the study.
Two commonly used quality assessment tools are the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) tool and the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklist. Both tools are designed to assess the quality of different types of studies, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies.
Example:
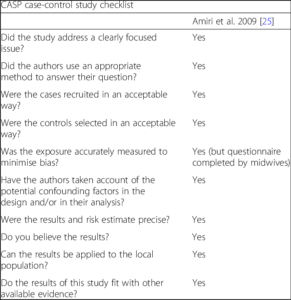
The CASP tool is a series of checklists that are used to evaluate the quality of studies based on factors such as the study design, sample size, and statistical analysis. The JBI tool is a comprehensive checklist that assesses a range of factors, including study design, methodology, and data analysis.

When using these tools, it is important to keep in mind that quality assessment is a subjective process and that different assessors may interpret the same evidence differently. It is therefore important to ensure that assessors are trained in the use of the tool and that there is consistency in the application of the tool across different studies.
Synthesizing the Findings
Synthesizing findings is an important step in research that involves analyzing and combining the results of multiple studies to draw conclusions or identify patterns.
Both content analysis and meta-analysis can be used to synthesize findings from multiple studies, but they differ in their approach and the types of data they analyze. Researchers should choose the most appropriate method based on their research question and the nature of the data they are synthesizing.
By focusing on a set of shortlisted studies, researchers can reduce the amount of data they need to analyze and increase the likelihood of identifying meaningful patterns or themes. Additionally, this approach allows researchers to focus on studies that are most relevant to their research question, which can help ensure the synthesis is focused and meaningful.
Once the shortlisted studies have been identified, researchers can use content analysis or meta-analysis to synthesize the findings. Content analysis involves analyzing the textual or visual data within each study to identify patterns or themes, while meta-analysis involves combining the numerical data from each study to estimate an overall effect size. Both methods can be useful depending on the nature of the data and the research question.
When synthesizing findings in a research study, it is important to draw on frameworks discussed in the literature review section. The literature review provides a comprehensive overview of existing research and identifies relevant theories, concepts, and frameworks that can help guide the analysis and interpretation of the findings.
Frameworks discussed in the literature review can help provide a structure for the synthesis of the findings. For example, if the research question is focused on exploring the factors that contribute to a particular behavior or outcome, a theoretical framework such as the Social Ecological Model can be used to guide the analysis of the findings. Similarly, if the research question is focused on identifying the key themes or patterns in the data, a thematic analysis framework such as Braun and Clarke’s six-step process can be used to guide the synthesis.
Using frameworks from the literature review can also help ensure that the synthesis is rigorous and transparent. By drawing on established frameworks, researchers can demonstrate that their analysis is grounded in established theory and methods, and that the findings are interpreted within a broader context of existing research. This can help increase the credibility and trustworthiness of the research findings.
To synthesize the findings and answer the research question, it is important to first summarize the main results of the study. The synthesis should highlight the key findings and their implications for the research question.
The ideal synthesis of findings will typically involve several steps. These include:
Overall, the ideal synthesis of findings will present a clear and concise overview of the research question, methodology, and main findings of the study, while also highlighting the implications of the results and identifying future research directions.
The appendices section is an important part of a systematic literature review (SLR) because it provides additional information and details that may not be suitable for inclusion in the main body of the review but are relevant to the research question or topic being studied.
The appendices may include, but are not limited to:
Including these details in the appendices section can increase the transparency and rigor of the review, and allow readers to assess the quality and validity of the review more easily.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
Writing the Dissertation
The final step in conducting a systematic literature review is to write your dissertation. Your dissertation should include an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. You should clearly state your research question, summarize the literature, describe your methodology, present your findings, and provide recommendations for future research.
In conclusion, writing a systematic literature review dissertation can be a daunting task, but by following these steps, you can successfully complete your dissertation. Remember to stay focused, be systematic, and critically evaluate the literature. With these tips, you can produce a high-quality dissertation that makes a meaningful contribution to your field of study.
How WritoSpark can help you with SLR ?
WritoSpark can offer a range of services to help with a systematic literature review, including:
Literature Search: We can assist in conducting a comprehensive literature search by using various electronic databases and other relevant sources. They can also help to identify relevant keywords and search terms to ensure that the search is comprehensive and focused.
Screening and Selection: We can assist in screening and selecting relevant studies based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. This can be done using software programs that help to manage the process and keep track of the studies that have been included and excluded.
Quality Assessment: We can help to assess the quality of the studies that have been included in the review. This involves evaluating the study design, sample size, data collection methods, and analysis techniques used in the studies.
Data Extraction: We can help to extract relevant data from the studies that have been included in the review. This involves developing a data extraction form and using it to extract data from each study.
Data Synthesis: We can help to synthesize the data that has been extracted from the studies. This involves analyzing the data and identifying common themes, patterns, and discrepancies.
Report Writing: We can help to write the systematic literature review report. This involves structuring the report, presenting the findings, and making recommendations for future research.
Overall, Writospark can offer support and guidance throughout the systematic literature review process. They can help to ensure that the review is conducted efficiently and accurately, and that the findings are presented in a clear and concise manner. This can be particularly helpful for students who are new to the process or who may have limited time or resources to complete the review themselves.
